A clinical trial phase is a part of the clinical research process that answers specific questions about whether treatments or other interventions that are being studied work and are safe.
- Phase I (Non -therapeutic, first-in-human) trials test the best way to give a new treatment and the best dose. It involves <50 participants
- Phase II (Exploratory) trials test whether a new treatment influences the disease. It involves 5-100 patients of either sex
- Phase III (Confirmatory) trials compare the results of people taking a new treatment with the results of people taking the standard treatment. It involves more than 300 patients (up to 3.000) of either sex
- Phase IV (Post-approval) studies are done using thousands of people after a treatment has been approved and marketed, to check for side effects that were not seen in the phase III trial.
- National Institute of Health (NIH)-National Cancer institute: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/clinical-trial-phase
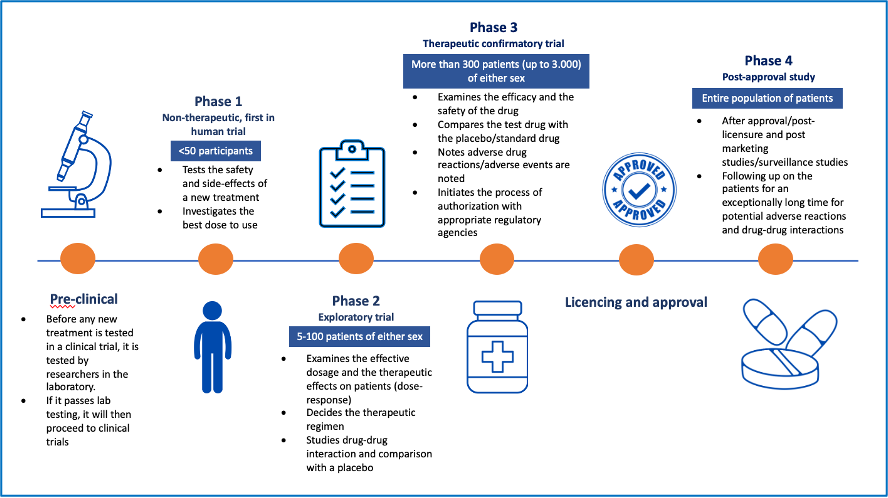
Adapted from Kandi V, Vadakedath S. Clinical Trials and Clinical Research: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2023 Feb; 15(2): e35077: https://assets.cureus.com/uploads/review_article/pdf/128436/20230317-1378-1d3buy1.pdf



